Can communication technologies applied in the areas of health and well-being improve the lives of small isolated European communities? This is the question that Victoria Ramos, who is a Senior Research Scientist in the Telemedicine Unit of the Carlos III Health Institute, looks to answer in the (Ideas MELting pot for TIC and Health science for Citizens in small communities). The project is financed through an open call for proposals within the European project of open science ORION, and is managed by the ISCIII’s Sub-directorate of International Research Projects.
The objective of the MELTIC project is to incorporate co-creation methodology into research activities in ICT in the areas of health and biomedicine so that they become more open, transparent and accessible, increase their social impact and therefore contribute to improving the quality of life of European citizens in small communities.
The co-creation methodology applied to research in Health and Well-being and Information and Communication Technologies has proven to be valid tool for studying the improvement of the quality of life of European citizens in small communities.
In this work, various challenges facing European politics are connected, such as depopulation, health, active aging, education, youth and climate change, and research is carried out in order to identify the current and future needs of these citizens with the purpose of innovating the use of existing public spaces and / or in building new ones.
The project has been carried out thanks to the setting up of transnational co-creation workshops, in which members of small communities with local profiles related to health and well-being have participated (patients, parents, doctors , nurses, associations of various types and decision-makers) in the , , and
Two main results have come out of the project, a Vademecum of 100 ideas for research in ICT in Health and Biomedicine in these communities and also, a technological proposal has been developed as a model of cooperation in rural communities.
The study proposed by MELTIC, together with the contributions of professionals, will also facilitate the identification of the potential impacts of new research ideas, as well as understanding the opportunities and risks that have not yet been systematically compared, discussed and evaluated. A longer-term experience or analysis still doesn’t exist, which means that a final evaluation concerning the Implications of ICT in small communities will require further study in the near future. Due to the rapid development and application of new technologies, there is a permanent need for monitoring and supporting the work of ICT researchers, urban designers and social agents. The stakeholder analysis and information provided directly from the MELTIC partners’ workplace sets out the context for the co-creation process.
Research in health and well-being through ICT
This work raises the question of how to use smart technologies to transform public spaces in small communities into people friendly human environments. The structure is designed around the relevance of inclusive and multidisciplinary co-creation and introduces the importance of integral development. A technical proposal on a model of citizen cooperation in small rural communities is presented. This will help us better understand (potential) interactions.
Dialogue and connections between people (as users) with the real and virtual world also open up new requirements in advanced knowledge, not only in new ways of collecting information, but also in how to interpret this data. In addition, there is an additional need to manage and disseminate the acquired knowledge. MELTIC analyses the current use and development of electronics, information technology and telecommunications and the relevance they have on a day-to-day basis, aggregating something new almost every day.
Co-creation processes during the research
The effectiveness of any effort made in promoting health and well-being depends on its ability to achieve and engage its intended goal. New information technology (IT) tools can be an important aid by adapting the intervention and the framework for action according to the relevant needs.
This is why, it is important and necessary to introduce co-creation processes that are developed, as in this case, through a participatory design [1], [2].
“It is important and necessary to introduce co-creation processes that are developed, as in this case, through participatory design”
In the MELTIC project, the co-creation process has been developed as follows. The workshops took place in both physical and virtual formats, depending on the health situation of each community due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and they were based on the following stages:
- A process to explore connected themes
- A joint conceptualization phase
- A contribution phase
- Visualization of the final ideas
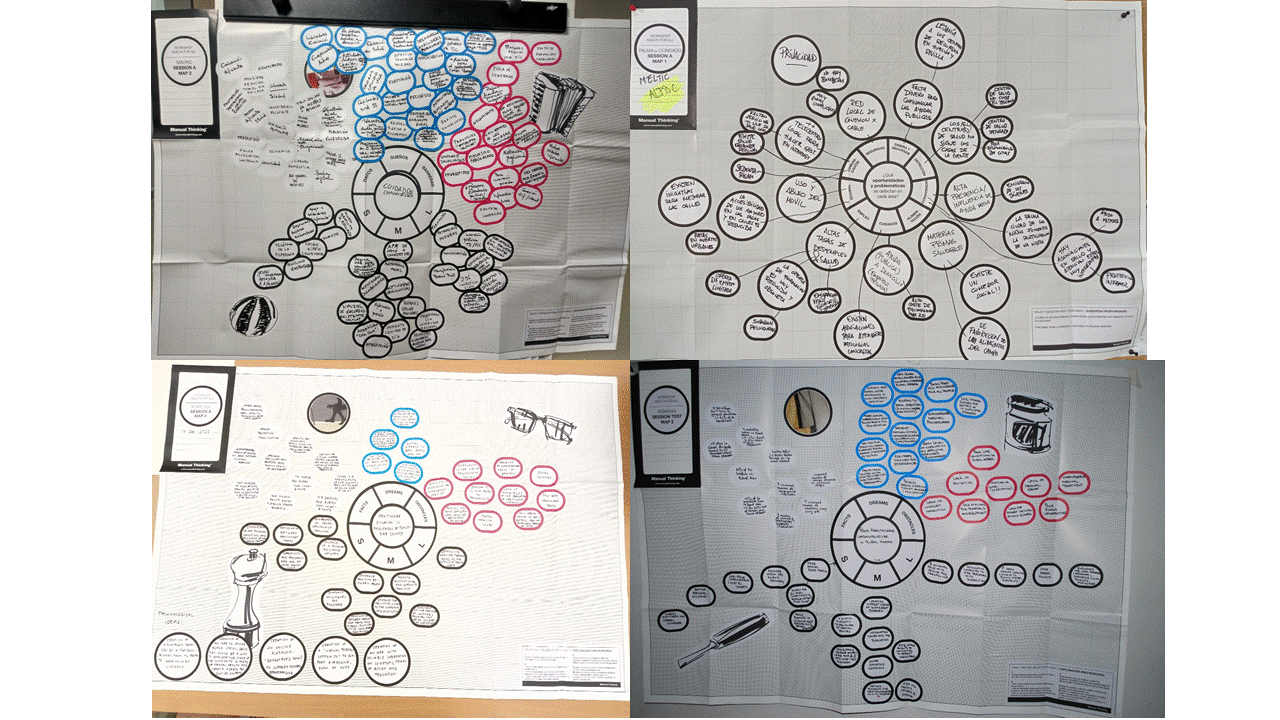
The profiles of the participants in the co-creation activities are represented below in Diagram 2:
In these workshops, each municipality has identified health-related problem areas, opportunities, and solutions for their region. The ideas have then been put together as a word map in order to discover their respective keywords.
Subsequently, they can be seen in the form of word clouds in which the repeated ideas are displayed in different sizes, with the key words standing out. The workshops have allowed us to find new ideas, while at the same time becoming familiar with the ideas of others and with the different Sustainable Development Goals as presented in Diagram 4.
Technological proposal: Digital eXperience Platform (DXP)
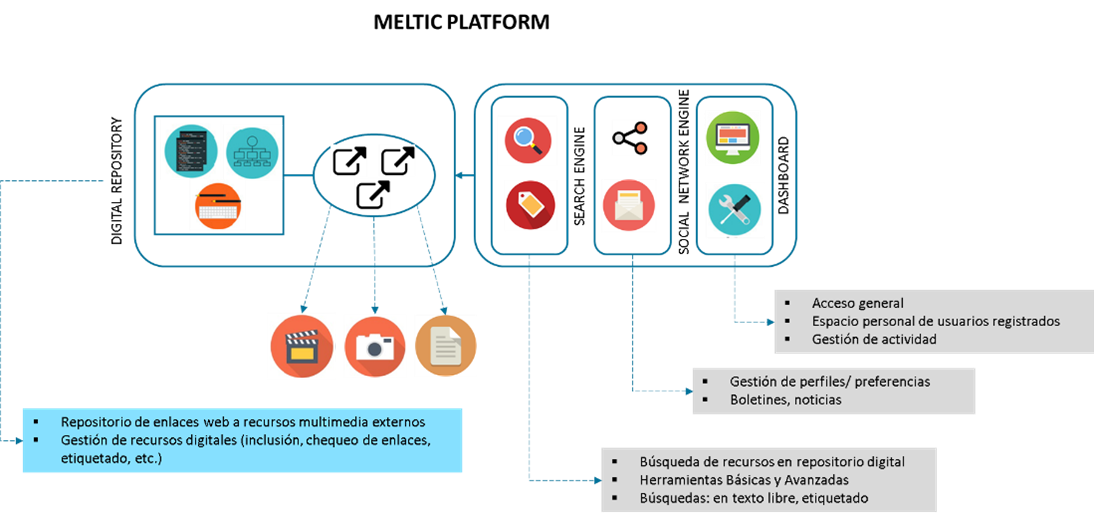
The MELTIC DXP platform is defined as an ICT infrastructure based on distributed open-source architecture following international standards, deployed in a virtual environment allowing for independence between services and hardware, and providing a service with a high level of availability, flexibility, scalability and security. The IT infrastructure, in terms of communication lines and mass storage, will be redundant, with all the security elements and safe access being made available in order to avoid service failures and unauthorized access.
The functionalities of the platform are conceived as modular components and / or micro services, with open interfaces, low coupling and high cohesion, which will provide security and high scalability in the services provided. Essentially, the micro services architecture implies the development of software as a set of small, modular services with unique processes, whose implementation is independent and that communicate with each other through a simple and well-defined mechanism.
- General access
- Personal space for registered users
- Activity management
- Profile/preference management
- Newsletters, reports
- Repository of web links to external multimedia resources
- Management of digital resources (inclusion, link checking, tagging, etc.)
To access the demonstrator
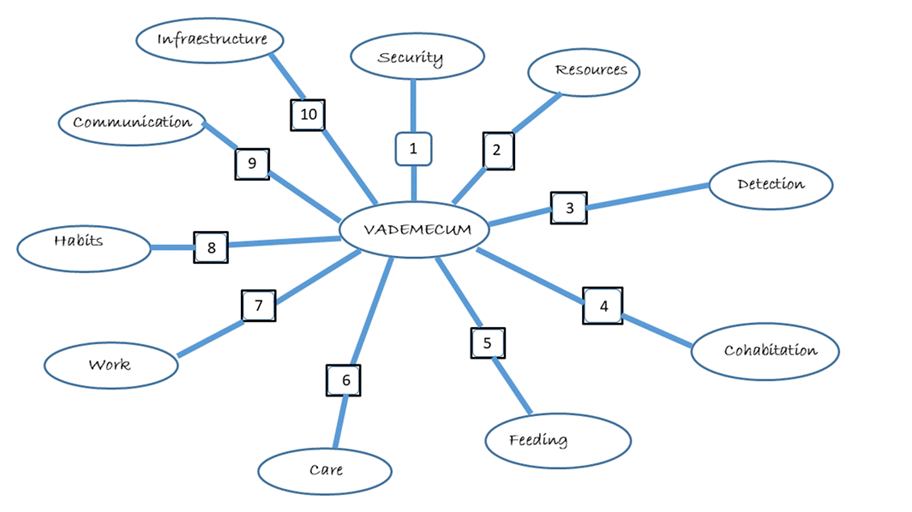
VADEMECUM
The ideas generated during the co-creation workshop were gathered together in a Vademecum of 100 Challenges for Health and Well-being in rural areas.
The partners carried out an exploratory study among the stakeholders and their areas of work, as well as looking at the spatial and social aspects in small and isolated communities that could be enriched by ICT.
Conclusions
Due to the rapid development of technologies and their application, there is a permanent need to monitor and support the work of ICT researchers, urban designers and social agents. Therefore, the analysis carried out by the participants in MELTIC, highlighted the fact that the use of Smart technologies in public spaces are creating ever increasing forms of interaction and social practices, in addition to creating new socio-spatial relationships and promoting interactions and communication between isolated and dispersed communities.
“New relationship scenarios drive the need to rethink social practices and the use of public spaces, which, in turn, can also influence the development of ICTs and their devices”
These types of new relationship scenarios drive the need to rethink social practices and the use of public spaces, which, in turn, can also influence the development of ICTs and their devices. Website-based interventions play a key role in fostering health and social care and supervision.
References
[1] Giorgi Rossi et al. “Using Cocreation to Dene Contents and Functions of a Smartphone App for Obesity Prevention in Childhood: Mixed Method Study Describing the Process.” JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020 Feb 21. PMID: DOI: 10.2196 / 16165
[2] Linda Mansson et al. “Co-creation with older adults to improve user experience of a smartphone self-test application to assess balance function” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17 (11), 3768; https://www.mdpi.com//17/11/3768
MELTIC project of Intituto de Salud Carlos III, with file TMPY 182/20, is founded through the European project ORION (Open Responsible research and Innovation to further Outstanding kNowledge), having won the open call for proposals: “Novel co-creation initiatives to open up research in life sciences and biomedicine” within the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program
The authors of the MELTIC project are: Victoria Ramos, Andrés Dochao, Roberto D´Amico, Gregory Duta and Anabella Caeiro.
![]() ORION has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement Nº 741527.
ORION has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement Nº 741527.